Glutathione Foods
Glutathione is a natural antioxidant that is found in many foods. It is a protein that is produced in the body. It is also found in certain foods and supplements. Glutathione has antioxidant properties, which are important for fighting against aging, oxidative stress, and assisting the body to prevent and fight chronic illnesses such as cancer.
Glutathione helps to maintain the integrity of cells and protects them from damage. It also helps to detoxify heavy metals, like mercury and lead, which can accumulate in the body over time. Glutathione is important for our overall health because it plays a key role in maintaining immune system function and protecting our cells from damage by free radicals or other environmental toxins.
Glutathione is a naturally occurring, powerful antioxidant found in the body and foods. It is a protein that is synthesized in the liver and kidneys. It has many important roles in the human body, including regulating cell growth, repairing DNA, and detoxifying harmful substances.
Some of the benefits of glutathione are: it protects against oxidative damage and DNA damage, boosts immunity by boosting production of white blood cells and antibodies, and helps fight inflammation by reducing levels of nitric oxide and prostaglandins that are linked to inflammation.
There are many forms of oral glutathione available in powder and pill form on the market today. Most of these formulations are not effective, because when they are taken orally, glutathione pills and powders are often digested by our stomach acids and are digested by our body before this important antioxidant can be absorbed into our blood stream."
A Closer Look at Glutathione
Glutathione is important for detoxification, immune system function, and healing.
The word glutathione comes from two Greek words:
gluta - meaning "glue."
thi - meaning "to produce."
Glutathione is a potent antioxidant that binds to toxins and free radicals in the body and makes them inert so they can be eliminated. Free radicals are molecules that have been damaged and have an unpaired electron in their outer atomic shell. Free radicals are also called "reactive oxygen species". Glutathione has a very large number of electrons in its outer atomic shell, and can donate an electron to the free radical, rendering free radicals inert, and subsequently unable to damage other molecules in neighboring tissues of our bodies. Glutathione does this without damaging it's own atomic stability.
More About the Chemical Make-Up of Glutathione
The body produces Glutathione when it breaks down the amino acid Cysteine.
Cysteine is an amino acid, and it is one of the building blocks for proteins. Proteins are responsible for cells, tissues, muscles, and other parts of the body. Cysteine plays a major role in helping to create enzymes that break down food, hormones that control important body functions such as blood pressure and sugar levels, and substances that promote healing.
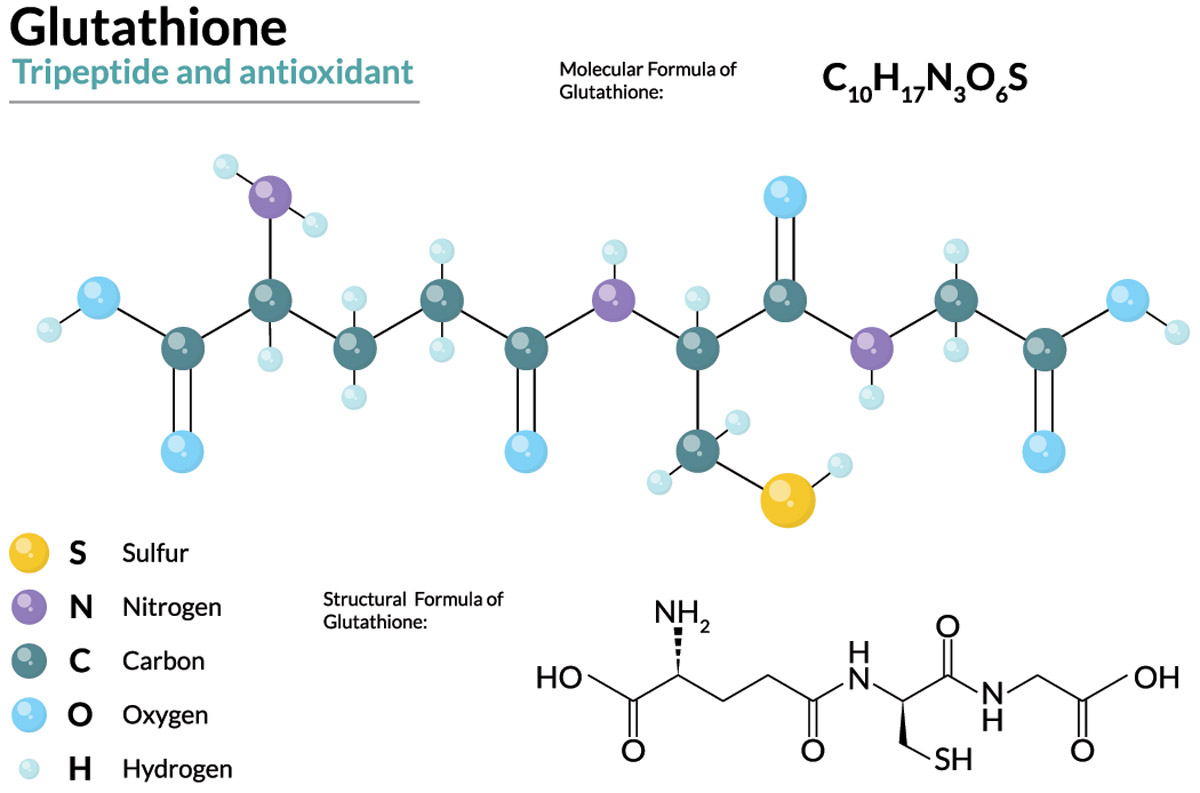
Glutathione is a tripeptide with the formula (Cys)Gly(Cys)Glu. It is synthesized in all living cells but cannot be stored and must be synthesized as needed. Glutathione consists of 3 amino acids: cysteine, glycine, and glutamate. Glutathione has several functions: it acts as an antioxidant by reacting with hydrogen peroxide; it detoxifies reactive oxygen species such as hydrogen peroxide; it regulates cellular redox reactions by controlling the cellular concentrations of glutathione.
Glutathione antioxidant properties also help to protect against inflammation by inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-alpha, IL-1 beta, and IL-6. TNF-alpha, IL-1 beta, and IL-6 are all implicated in various inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, Crohn's disease, inflammatory cancers, and diseases of advanced aging such as progeria¹ and increase in our bodies as we age and when our body cannot produce adequate amounts of glutathione.
How Does Eating Glutathione-rich Diet Affect Health & Performance?
Glutathione is a naturally occurring tripeptide that is synthesized in the human body. It has been shown to play a key role in detoxification. A glutathione-rich diet is an important aspect of anti-aging and anti-cancer diets. It is synthesized from three amino acids: cysteine, glutamic acid, and glycine. Cysteine is the most important amino acid for glutathione synthesis, as it has a high sulfur content and can cross the blood-brain barrier easily. Since the brain, heart, and liver need enormous amounts of the antioxidant glutathione, it is important to provide foods that are rich in the amino acid cysteine, the critically important precursor for glutathione.
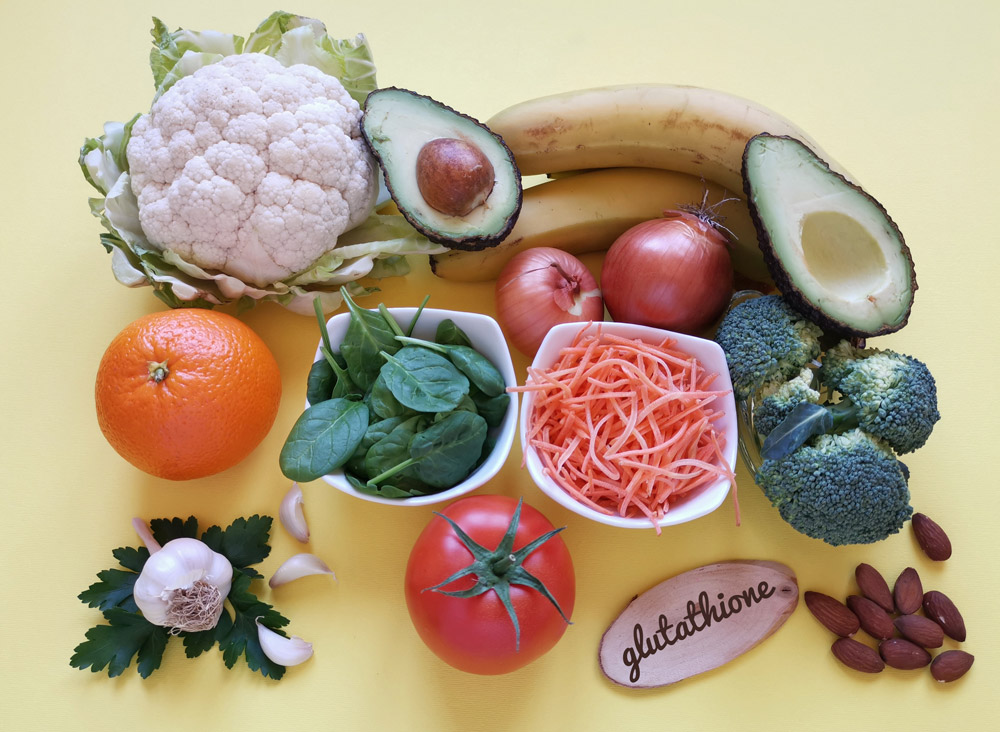
The most common food sources of cysteine, the important precursor of glutathione, are eggs, broccoli, onions, garlic, and cabbage. Other foods rich in cysteine include red meat, poultry, seafood like shrimp and crabmeat, and nuts.
A diet rich in glutathione foods will help protect your body from oxidative stress and chronic illnesses like cancer. Some foods are that are great for Glutathione are:
Asparagus
Avocado
Beets
Broccoli
Carrots
Cabbage
Citrus Fruits
Garlic
Grapefruit
Kiwi Fruit
Lemons and Limes
Mangoes

A Higher Glutathione Level:
Improves Immune Response
Reduces Physical and Mental Fatigue
Enhances Mental and Physical Performance
Accelerates Physical and Mental Recovery from Exercise
Increases Longevity
Reduces Oxidative Stress
Reduces Intercellular Inflammation
Combats Accelerated Aging
Delays the Onset of Diseases of Aging
Removes Chemical Toxins from Cells
Critical for Oxygen Transfer
The glutathione system is the most important antioxidant defense system the body can have. When Glutathione is found in all body cells, it protects them from free radicals and oxidative stress damage.
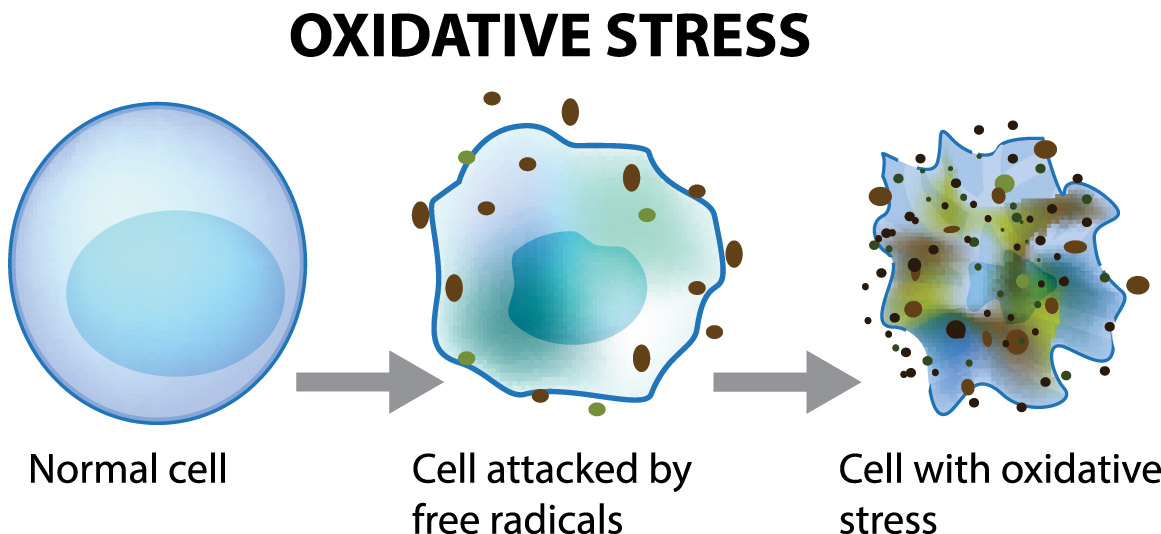
The damage caused by free radicals is called oxidative stress. Oxidative stress can lead to a number of diseases and conditions, including cancer, heart disease, stroke, and Alzheimer's disease.
What are Free Radicals?
Free radicals are molecules that contain an unpaired electron, which can cause damage to cells in the body, which can lead to accelerated aging, and degenerative diseases such as cancer over time. There are many ways of preventing free radicals, such as getting enough sleep, exercising, and eating a balanced diet.
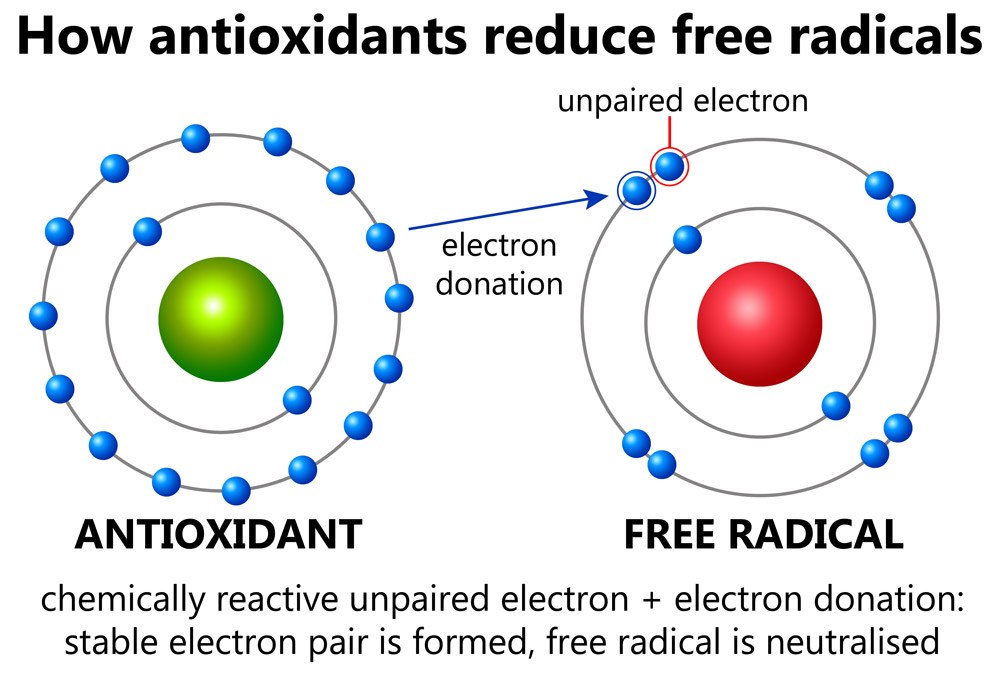
Free radicals are created when we breathe, eat, and drink. They also come from the sun’s rays and industrial pollution. But these free radicals can be neutralized by antioxidants. Free radicals are a type of molecule that has an unpaired electron in their outer orbit. This causes it to seek out other molecules to steal their electrons, and in the process, it damages them.
The damage done to cells by free radicals is called oxidative stress or oxidative damage. This can lead to cell death which can cause many diseases like cancer, diabetes, and heart disease.
There are many foods that have antioxidants, such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, that help with this issue because they contain compounds that help stop the oxidation process by donating electrons back to the free radical before it attacks.
What is the Role of Antioxidants in Mitigating the Damage from Free Radical Attacks?
Antioxidants are essential for the maintenance of good health. They help to protect cells from the damage caused by unstable molecules called free radicals.
The best way to get antioxidants is through a healthy diet, which includes plenty of fruits and vegetables, nuts, beans, whole grains, and olive oil; however, some people may need a little more help in order to meet their daily requirements.

There are two types of antioxidant supplements: those containing vitamins C or E and those containing a combination of vitamins C, E, and beta-carotene (a type of vitamin A).
Antioxidants are substances that can help to prevent and repair the damage done by free radicals. Free radicals are highly reactive molecules that can cause damage to cells, tissues, and DNA. Antioxidants work by donating an electron to free radical molecules, neutralizing their reactivity. But when an antioxidant other than glutathione donates an electron, it becomes unbalanced, and must rely on glutathione to donate one of it's electron to become balanced and usable by our bodies once again.
The body needs an adequate supply of antioxidants in order to function properly. Antioxidants are healthy compounds that fight against free radicals and help to prevent certain diseases. Foods rich in antioxidants include tomatoes, strawberries, blueberries, and spinach.
Some of the ways to protect your body from free radical damage in the first place are by:
Eating a healthy diet
Drinking plenty of water
Exercising regularly
Maintaining an optimal weight
Free radicals are molecules that have an unpaired electron. They can be formed from natural processes or from environmental influences such as pollution, radiation, and cigarette smoke. Free radicals can damage cells by stealing electrons or attaching themselves to the molecules in the cell.
Antioxidants are molecules that help remove free radicals from the body. There are two types of antioxidants: endogenous (produced by the body) and exogenous (produced outside of the body).
How Immunocal Can Help
Now that we understand all of this, what free radicals are, where they come from, what Glutathione is, and why we need it, we need to look at ways to improve our Glutathione intact. That's where the Immunocal supplement can help.
Immunocal is a patented, natural complex carbohydrate that provides the nutritional foundation for the human immune system. It has been clinically shown to support healthy immune function, enhance energy and vitality and reduce fatigue. It contains a unique blend of high-quality proteins, essential fats, and carbohydrates, which are vital for maintaining optimal health.
Immunocal is a nutritional supplement made from a patented, proprietary blend of undenatured whey protein. The immune system is the body's natural defense mechanism against infections and diseases. It can be compromised by stress, poor diet, environmental factors, and other illnesses. Immunocal has been clinically shown to support the immune system in healthy adults.
What are the Health Benefits of Using Immunocal?
The first benefit of Immunocal is that it provides immune system support. The immune system is the body's natural defense system against bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites, and other foreign invaders. This supplement will help to improve your immune response to illness or infection. Immunocal has been clinically proven to significantly increase the levels of glutathione in the body.
The second benefit of Immunocal is that it contains the precursors for the potent master antioxidant glutathione. The antioxidant glutathione has been shown to reduce the severity and duration of colds, flu, fever blisters (herpes simplex), shingles (herpes zoster), and bronchitis in clinical studies.
The third benefit of Immunocal is that it promotes better digestion. It supports healthy digestion by increasing stomach acid production, which helps break down foods to be absorbed properly.
Scientific research has clearly shown that there are many factors that can affect our immune system. One important factor that can affect immunity is stress. When you are stressed, your body produces more cortisol, suppressing your immune system. There are also emotional and mental factors that can affect immunity, such as anger or depression. Sports and exercise, getting sufficient sleep, detaching from electronic devices and getting out in nature are some things you can do that will help you reduce stress and improve your overall health.
Be sure that you exercise regularly, maintain a healthy diet of foods rich in antioxidants and Glutathione, and take supplements such as Immunocal to protect yourself from disease.